Dreaming of a vacation getaway or a savvy investment property? Buying a second home can be a rewarding experience, offering both personal enjoyment and potential financial gains. However, navigating the complexities of a second home purchase requires careful planning and strategic decision-making. This article will explore smart strategies for buying your second home, providing valuable insights into financing options, market analysis, and legal considerations. From assessing your financial readiness to identifying the ideal location, we’ll cover the essential steps to make your second home dream a reality. Whether you’re looking for a tranquil retreat or a lucrative investment, understanding the intricacies of the second home market is crucial for smart buyers.
The process of acquiring a second home differs significantly from purchasing a primary residence. Factors such as rental potential, property management, and tax implications must be carefully considered. This guide will delve into smart strategies for securing the best possible financing terms, negotiating effectively, and understanding the legal ramifications of second home ownership. We’ll equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions, avoid common pitfalls, and ultimately secure a second home that aligns perfectly with your goals and budget. By employing these smart strategies, you can confidently navigate the market and maximize your investment potential.
Evaluating Your Financial Readiness
Purchasing a second home is a significant financial undertaking. Before embarking on this exciting venture, it’s crucial to thoroughly assess your financial standing.
Begin by evaluating your current debt-to-income ratio. A lower ratio indicates a stronger financial position and a greater likelihood of loan approval. Next, determine the down payment you can comfortably afford. A larger down payment can secure better loan terms and reduce your monthly mortgage payments.
Finally, factor in ongoing costs such as property taxes, insurance, potential repairs, and utility bills. Creating a realistic budget that encompasses these expenses is essential for successful second home ownership.
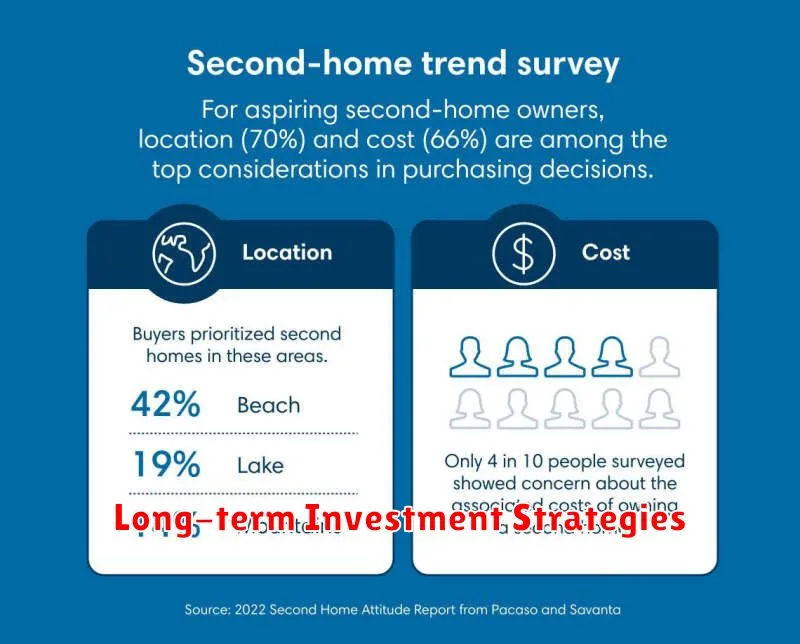
Deciding on the Ideal Location
Choosing the right location is arguably the most critical decision when buying a second home. It directly impacts your enjoyment, potential rental income, and future resale value. Carefully consider your primary goals for this purchase.
A vacation home near recreational activities requires different considerations than an investment property. Think about proximity to family, friends, and amenities important to you. Research the local market trends and consider the long-term growth potential of the area.
Accessibility is another key factor. Evaluate travel time and costs from your primary residence. If you plan to rent the property, convenient access for potential renters will be essential.
Assessing Market Conditions
Before diving into your second home purchase, thoroughly research the prevailing market conditions. A buyer’s market offers more negotiating power, potentially lower prices, and a wider selection of properties. Conversely, a seller’s market can mean higher prices, increased competition, and fewer available homes.
Key factors to consider include:
- Inventory levels: A high inventory suggests a buyer’s market, while low inventory often signals a seller’s market.
- Median home prices: Track price trends to understand if the market is appreciating or depreciating.
- Days on market (DOM): A higher DOM can indicate a buyer’s market, while a lower DOM suggests strong seller demand.
- Interest rates: Rising interest rates can cool down a market, while lower rates can stimulate activity.
Considering Rental Potential

A key factor in purchasing a second home is evaluating its rental potential. This can significantly offset ownership costs and even generate passive income.
Assess the local rental market. Is there consistent demand for short-term or long-term rentals? Research comparable properties and their rental rates to estimate potential income.
Factor in expenses like property management fees, insurance, taxes, and maintenance when calculating your potential return on investment. Location plays a crucial role. Proximity to attractions, amenities, and transportation hubs enhances rental desirability.
Understanding Tax Implications
Purchasing a second home presents various tax implications that are crucial to understand. These can significantly impact your overall financial position. Proper planning and awareness of these potential deductions can help optimize your investment.
Mortgage interest deduction: You may be able to deduct the interest paid on your mortgage, subject to certain limits. Consult a tax professional for current regulations.
Property taxes: Similar to your primary residence, property taxes paid on a second home are generally deductible.
Rental income: If you plan to rent out your second home, the income generated will be taxable. However, you can also deduct expenses associated with renting, such as maintenance and depreciation.
Exploring Financing Options
Securing financing for a second home requires careful consideration of various options. Loan requirements often differ from primary residences, frequently involving larger down payments and higher interest rates.
A home equity loan or HELOC against your primary residence can be a viable option, offering access to existing equity. However, this puts your primary home at risk should you encounter financial difficulties.
Traditional mortgages specifically for second homes are also available. These loans require a thorough assessment of your financial standing, including debt-to-income ratio and credit score.
Finally, explore cash-out refinancing your primary residence. This allows you to access your equity and consolidate debt, potentially at a lower interest rate. However, extending the term of your loan may increase overall interest paid.
Maintenance and Management Responsibilities
Owning a second home comes with inherent maintenance and management responsibilities. Regular upkeep is essential to preserve the property’s value and ensure its enjoyable use. This includes tasks like landscaping, cleaning, and routine repairs.
If you plan to rent out your second home, property management becomes a crucial aspect. You’ll need to handle tenant inquiries, collect rent, and address any maintenance issues promptly. Consider whether you’ll manage the property yourself or hire a property management company.
Budgeting for these expenses is paramount. Factor in potential costs for repairs, cleaning, property taxes, insurance, and potential management fees. A well-defined budget will help you avoid financial surprises and ensure a smooth second home ownership experience.
Planning for Retirement Living
A second home can serve as a stepping stone to retirement. When considering a purchase, think about its long-term suitability. Will it meet your future needs as you age?
Accessibility is key. Consider single-story homes or those with elevators. Think about proximity to healthcare and other essential services. Factor in the maintenance requirements. A smaller, more manageable property might be preferable in the long run.
Finally, assess the financial implications. Can you comfortably afford the property, including taxes, insurance, and potential upkeep, on a fixed retirement income? Planning ahead will ensure a smooth transition into a comfortable retirement.
Insuring Your Second Home
Insuring a second home requires careful consideration, as it differs from insuring a primary residence. Location plays a crucial role. Properties in high-risk areas, such as coastlines prone to hurricanes or earthquake zones, will likely have higher premiums. The type of property also impacts insurance costs. A condo generally requires less coverage than a standalone house.
Usage is another key factor. If you plan to rent out your second home, you’ll need a specific landlord policy. This policy covers potential liabilities and damages caused by renters. If the property is primarily for personal use, a standard homeowner’s policy with adjustments for a second home might suffice. Consult with an insurance professional to determine the right coverage for your individual needs and circumstances.
Long-term Investment Strategies
Purchasing a second home can be a significant investment. Adopting a long-term perspective is crucial for maximizing returns and mitigating risks.
Rental Income: Consider the potential for consistent rental income. Factor in location desirability, property management costs, and potential vacancy periods.
Property Appreciation: Real estate generally appreciates in value over time. Research historical market trends and projected growth in your chosen area.
Diversification: A second home can serve as a valuable asset for portfolio diversification, spreading investment risk beyond stocks and bonds.

